Cybersecurity Risk: Statistics and Trends 2023
Cybersecurity has become a key focus for businesses in 2023 as 2022 saw security breaches hit record levels.

2022 was a record year for data breaches and cybercrime. Companies in every sector were affected. Some of the more notable cyberattacks include:
- 24th November – 5,485,635 Twitter user records were made available for free on a hacker forum, due to an API vulnerability.
- 19th October – More than 548,000 Microsoft users were exposed in the BlueBleed data leak due to a misconfigured endpoint.
- 22nd September – 9.8 million customers had data stolen from Australian telecoms company, Optus.
- 15th September – Uber’s system was breached by a notorious hacker known as “Nwave” using a social engineering hack. The cybercriminal contacted an Uber employee pretending to be an IT professional to gain login details. This came after another breach at the firm in 2016 when 57 million Uber users were affected.
- 12th May – The UK’s health service, the NHS, was brought to a standstill for several days during the WannaCry cyberattack.
- 17th April – Costa Rica suffered a ransomware attack that affected 29 public institutions, including the ministries of finance and social security.
Tip of the iceberg
The above are just some high-profile examples. Research has found that cybercriminals can penetrate 93% of company networks and gain access to local network resources. SMBs are less likely to report breaches when they happen, as it can be negative for their reputation, but small businesses are also more likely to underestimate the impact of a breach.
Attacks increased by 600% during the pandemic, when companies rushed to put in the IT infrastructure to allow for remote working and a distributed workforce. In doing so, many were left open to cyberattack. And since the onset of the war in Ukraine, Russian-based phishing attacks against business email addresses in Europe and the US have increased eight-fold.
The increased threat level means more businesses are taking cybersecurity seriously. 78% of SMBs are saying that they are increasing in investment in cybersecurity in the coming year. However, 67% of these feel they do not have the in-house skills to deal with data breaches.
This is one of the reasons that more companies are opting to outsource security as part of a wider Managed IT strategy.
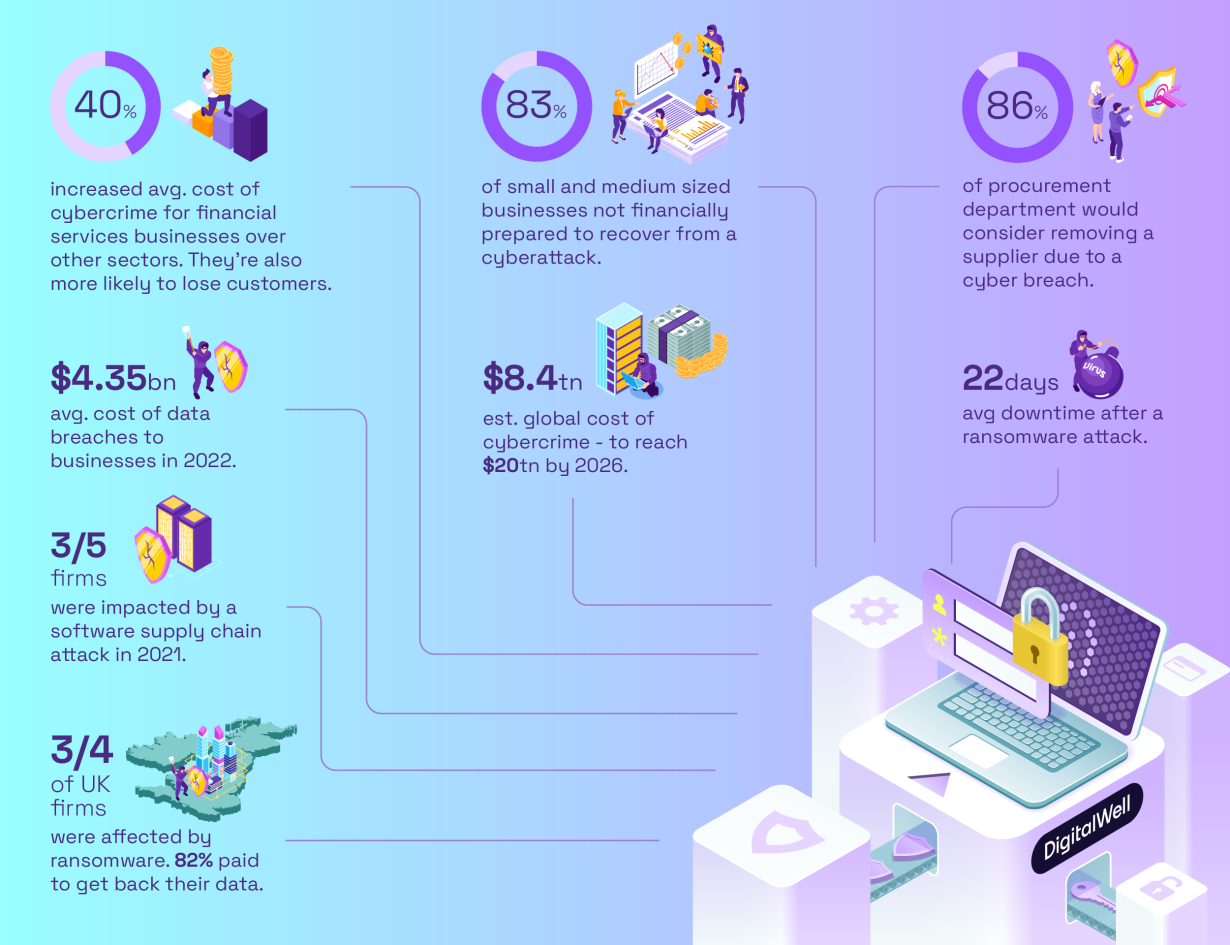
The costs of cybercrime
It makes sound business sense, given the potential risks and costs. Any downtime can be costly for a business. If private user data is leaked, then the reputational damage can lead to massive loss of business. The loss of intellectual property, such as a product design can be devastating, especially in formulative stages of a start-up.
Managed IT can help with cybersecurity
In 2023, companies need more than a firewall, a backup and an antivirus protect their businesses against cybercrime. The cybersecurity industry saw a wave of alerts for new malware strains and ransomware groups in March 2023. Most businesses don’t have the in-house resources, or the skills needed to deal with this rapidly evolving cybersecurity landscape. Patching, for example, isn’t a simple task for an in-house IT team, especially within large organisations, and it’s vital for companies to stay abreast of how malware is adapting to bypass security detection systems
Managed IT services can fill the gap, creating up-to-date solutions and actively managing solutions that take care of the risk.
In the follow-up to this article, we’ll be looking at some of the steps you can take to protect your business and at some of the ways Managed IT can help protect your business in what is set to be another very busy year for the cybersecurity industry.
In the meantime, to discover how DigitalWell’s Managed IT solutions can help your business with cybersecurity risk management, get in touch.


